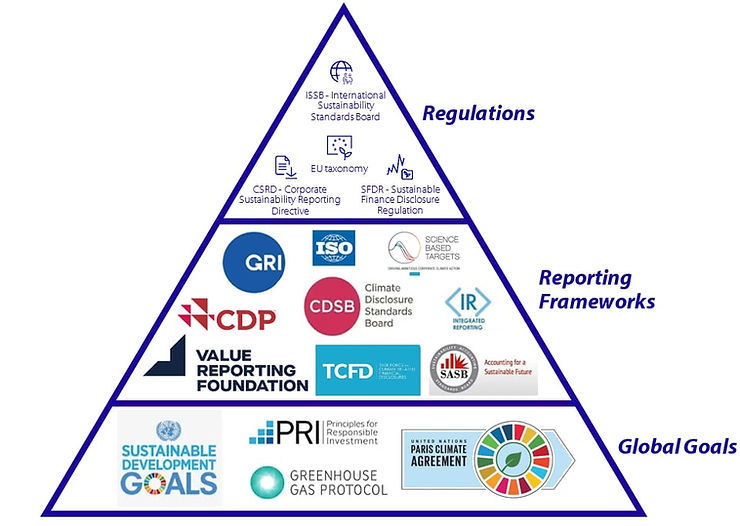
ISSB reports on several partnerships, including with GHG Protocol, CDP, TNFD and GRI.
- Art Dam
- Jun 24, 2024
- 1 min read
Today is Tuesday, 25 June 2024.
Accounting regulators seem busy these days, times of climate oddities getting increasing attention across the global.
Yesterday we posted about the North American FASB, Financial Accounting Standards Board, new technical project aiming the proper accounting recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure requirements for Environmental Credit Obligation (ECO) liabilities, “Noncompliance Credits” (i.e. voluntary carbon credits) and their Fair Value Measurement.
Today the news relates to International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB), responsible for developing International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Sustainability Disclosure Standards, detailing developments in strategic relationships with Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) and Global Reporting Initiative (GRI).
Not to mention support already received from IOSCO, the International Organization of Securities Commissions and the so called TIG, Transition Implementation Group on IFRS S1 and IFRS S2, with members from several countries all over the World.
Besides promoting consistency, a key objective of these partnerships is reducing the complexity - cost and effort - of multiple sources of sustainability reporting initiatives, while building on the established expertise and practices.
As a specific example the GHG Protocol standards, a vital tools to measure greenhouse gas emissions consistently and comparably, they were embedded in, among others, the IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures released last year.
All in all, this means that corporate reporting is more and more incorporating climate impact related elements.
This trend is positive in terms of comparability and audibility of companies, pushing for enhanced integrity.
Click at the image below for a thorough ISSB press release. And here for the specific one by GHG Protocol.